Mendel’s pea plant experiments worksheet answers provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the groundbreaking work of Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics. This worksheet delves into the significance of Mendel’s experiments, the traits he studied, and the experimental methods he employed to unravel the fundamental principles of inheritance.
Through a series of carefully designed experiments, Mendel laid the foundation for our understanding of how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. His discoveries have had a profound impact on the fields of biology, medicine, and agriculture, and continue to shape our understanding of the genetic basis of life.
1. Mendel’s Pea Plant Experiments
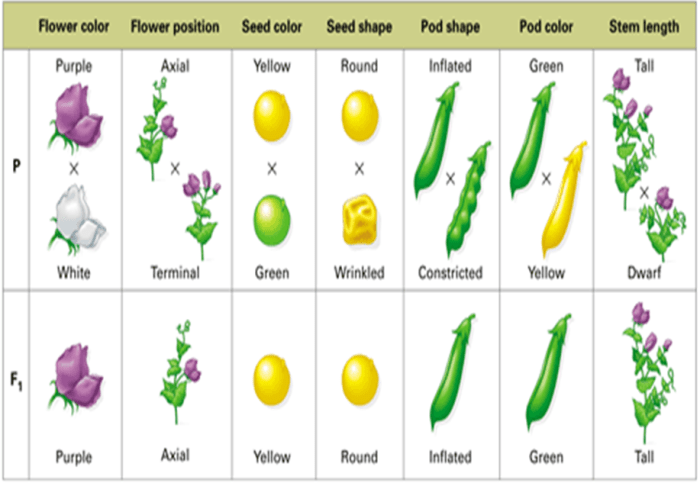
Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for modern genetics. He studied seven distinct traits in pea plants, including seed shape, seed color, flower color, and plant height. Mendel used a controlled experimental approach, cross-fertilizing pea plants with different traits and observing the inheritance patterns in their offspring.
Traits Mendel Studied, Mendel’s pea plant experiments worksheet answers
- Seed shape: round or wrinkled
- Seed color: yellow or green
- Flower color: purple or white
- Plant height: tall or short
- Pod shape: inflated or constricted
- Pod color: green or yellow
- Flower position: axial or terminal
Experimental Methods
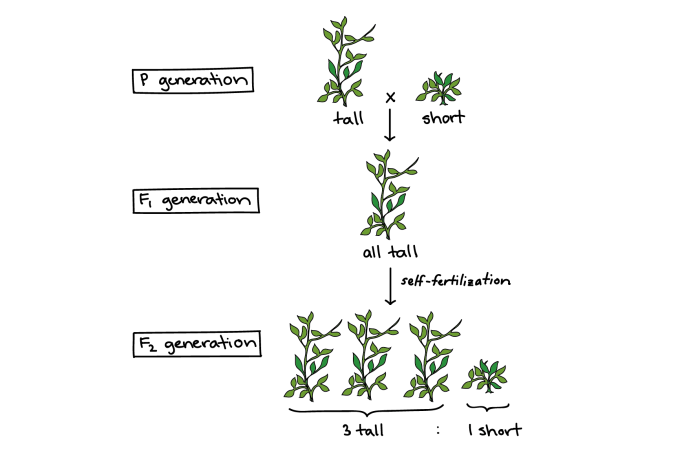
- Used pure-bred pea plants with known traits
- Crossed plants with contrasting traits (e.g., round vs. wrinkled seeds)
- Observed and recorded the traits of the offspring (F1 generation)
- Self-fertilized the F1 generation and observed the traits of the F2 generation
2. Punnett Squares: Mendel’s Pea Plant Experiments Worksheet Answers
Definition and Purpose
Punnett squares are diagrams used to predict the probability of offspring inheriting specific traits. They are based on the principles of Mendelian inheritance.
Using Punnett Squares
- Write the alleles of one parent along the top row and the other parent along the left column
- Fill in the squares with the possible combinations of alleles
- The genotypes of the offspring are determined by the alleles in each square
Example
| A | a | |
|---|---|---|
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
This Punnett square shows the possible genotypes of offspring from parents with genotypes AA and aa. The offspring can have genotypes AA, Aa, or aa.
3. Dominant and Recessive Alleles
Definition
Dominant alleles are alleles that are expressed in the phenotype of an individual even if only one copy of the allele is present. Recessive alleles are alleles that are only expressed in the phenotype if two copies of the allele are present.
Relationship
In a heterozygous individual (one dominant and one recessive allele), the dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele. The dominant allele is represented by an uppercase letter, and the recessive allele is represented by a lowercase letter.
Examples
- Brown eye color (dominant) over blue eye color (recessive)
- Tall plant height (dominant) over short plant height (recessive)
- Normal blood clotting (dominant) over hemophilia (recessive)
4. Genotype and Phenotype

Definition
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an individual.
Relationship
The genotype determines the phenotype, but the phenotype can be influenced by environmental factors. For example, two individuals with the same genotype may have different phenotypes if they are raised in different environments.
Table of Pea Plant Traits
| Trait | Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|
| Seed shape | RR | Round |
| Seed shape | Rr | Round |
| Seed shape | rr | Wrinkled |
| Seed color | YY | Yellow |
| Seed color | Yy | Yellow |
| Seed color | yy | Green |
Q&A
What is the significance of Gregor Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
Mendel’s experiments established the fundamental principles of inheritance, providing the foundation for our understanding of how traits are passed down from one generation to the next.
What traits did Mendel study in his pea plants?
Mendel studied seven distinct traits in pea plants, including seed shape, seed color, flower color, pod shape, pod color, plant height, and flower position.
How did Mendel use Punnett squares to predict the probability of offspring inheriting specific traits?
Punnett squares are a visual representation of the possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited from each parent. By using Punnett squares, Mendel was able to calculate the probability of offspring inheriting specific combinations of traits.