Foamy macrophages and fat globules breast – Foamy macrophages and fat globules are significant histological features in breast tissue, playing crucial roles in understanding breast diseases and aiding in the diagnosis of breast cancer. This article delves into the pathological significance of foamy macrophages, the diagnostic implications of fat globules in breast biopsies, and the histological analysis of these components.
The presence of foamy macrophages and fat globules in breast tissue provides valuable insights into the development and progression of breast diseases. Their histological characteristics and distribution patterns contribute to the differential diagnosis of breast lesions, enabling accurate and timely diagnosis.
Pathological Significance of Foamy Macrophages in Breast Tissue
Foamy macrophages are specialized immune cells found in breast tissue. Their presence is typically associated with various pathological conditions.
Role in Breast Disease Development
Foamy macrophages contribute to the development of breast diseases through several mechanisms:
- Inflammation: Foamy macrophages release inflammatory cytokines, promoting chronic inflammation in breast tissue.
- Tissue remodeling: They secrete enzymes that degrade extracellular matrix components, leading to tissue remodeling and fibrosis.
- Tumor progression: Foamy macrophages can promote tumor growth by suppressing anti-tumor immune responses and facilitating angiogenesis.
Associated Breast Diseases
Foamy macrophages are associated with a range of breast diseases, including:
- Fibrocystic breast disease: Benign breast condition characterized by cysts and fibrotic tissue.
- Breast cancer: Foamy macrophages are often present in breast cancer tissue, particularly in invasive ductal carcinoma.
- Inflammatory breast cancer: A rare and aggressive form of breast cancer with a high density of foamy macrophages.
Diagnostic Implications of Fat Globules in Breast Biopsy
Fat globules are lipid droplets found in breast tissue biopsies. Their presence has significant diagnostic implications.
Significance in Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Fat globules can aid in the diagnosis of breast cancer, particularly in the following scenarios:
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma: Presence of fat globules within tumor cells is a characteristic feature of this type of breast cancer.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ: Fat globules may be found in the cytoplasm of neoplastic cells in this non-invasive breast cancer.
- Apocrine carcinoma: This rare breast cancer is characterized by the presence of abundant fat globules within tumor cells.
Other Breast Lesions
Fat globules can also be present in other breast lesions, such as:
- Benign breast cysts: Fat globules may be seen within the cyst fluid.
- Fat necrosis: Trauma or surgery can lead to the formation of fat globules in breast tissue.
Histological Analysis of Foamy Macrophages and Fat Globules
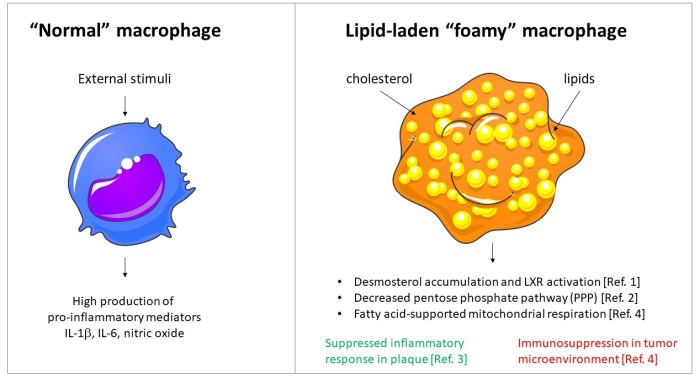
Histological techniques are used to identify and characterize foamy macrophages and fat globules in breast tissue.
Techniques for Identification, Foamy macrophages and fat globules breast
Foamy macrophages can be identified using the following techniques:
- Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining: Foamy macrophages appear as large cells with abundant pale cytoplasm.
- Oil Red O staining: This stain specifically highlights lipid droplets, including those present in foamy macrophages.
Fat globules can be identified using the following techniques:
- H&E staining: Fat globules appear as clear, round structures within cells.
- Sudan III staining: This stain selectively stains fat droplets, making them easily visible under a microscope.
Criteria for Normal and Abnormal Foamy Macrophages
Distinguishing between normal and abnormal foamy macrophages is crucial:
- Normal: Small number of foamy macrophages with a regular appearance and distribution.
- Abnormal: Increased number of foamy macrophages, with enlarged size, irregular shape, and atypical distribution.
Differential Diagnosis of Breast Lesions Based on Foamy Macrophages and Fat Globules: Foamy Macrophages And Fat Globules Breast
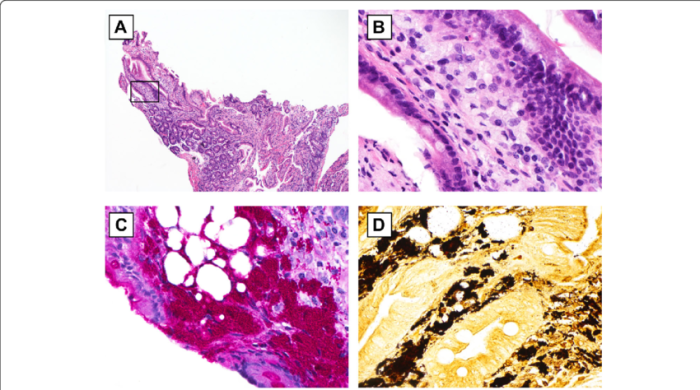
| Lesion | Foamy Macrophages | Fat Globules | Differential Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrocystic breast disease | + | + | Benign condition with cysts and fibrosis |
| Infiltrating ductal carcinoma | ++ | + | Invasive breast cancer with tumor cells containing fat globules |
| Lobular carcinoma in situ | + | + | Non-invasive breast cancer with fat globules in neoplastic cells |
| Fat necrosis | + | ++ | Non-cancerous condition with abundant fat globules |
Clinical Management of Breast Diseases Associated with Foamy Macrophages and Fat Globules
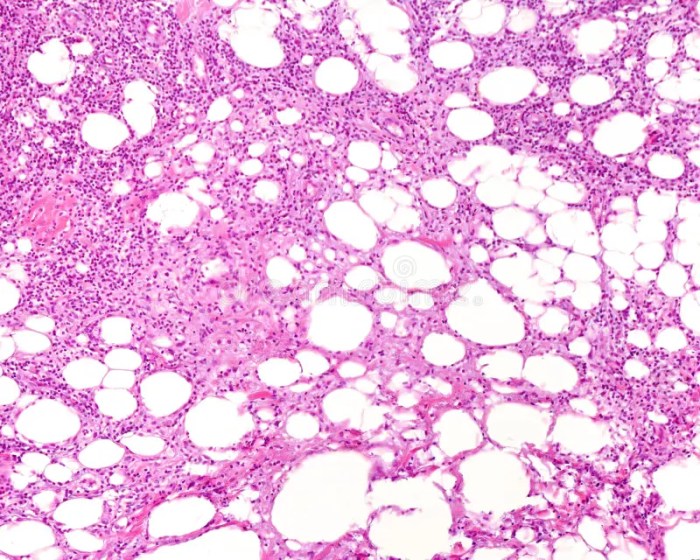
Clinical management of breast diseases associated with foamy macrophages and fat globules involves a multidisciplinary approach.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques, such as mammography and ultrasound, play a crucial role in the diagnosis and monitoring of these diseases.
Treatment Options
Treatment options vary depending on the underlying disease:
- Fibrocystic breast disease: Conservative management with lifestyle modifications and medications.
- Breast cancer: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy, as appropriate.
- Fat necrosis: Observation or surgical excision if necessary.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of foamy macrophages in breast tissue?
Foamy macrophages are immune cells that engulf lipid droplets, resulting in a foamy appearance. Their presence in breast tissue is associated with inflammation, chronic diseases, and certain types of breast cancer.
How can fat globules aid in the diagnosis of breast cancer?
Fat globules in breast biopsies can indicate the presence of invasive breast cancer. The size, distribution, and staining patterns of fat globules help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions.
What histological techniques are used to identify foamy macrophages and fat globules?
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is commonly used to visualize foamy macrophages and fat globules in breast tissue. Immunohistochemistry and lipid stains can provide further characterization.