Unit 6 imperialism from 1750 to 1900 answers – Unit 6: Imperialism from 1750 to 1900 Answers delves into the intricate tapestry of European expansionism and its profound impact on the world. This comprehensive resource provides a detailed exploration of the motivations, methods, and consequences of imperialism, offering a nuanced understanding of this transformative period.
From the factors driving European expansion to the diverse forms of colonialism practiced, this unit unravels the complex interplay between colonizers and colonized, shedding light on the profound impact of imperialism on societies, economies, and cultures across Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
European Expansion and Colonialism
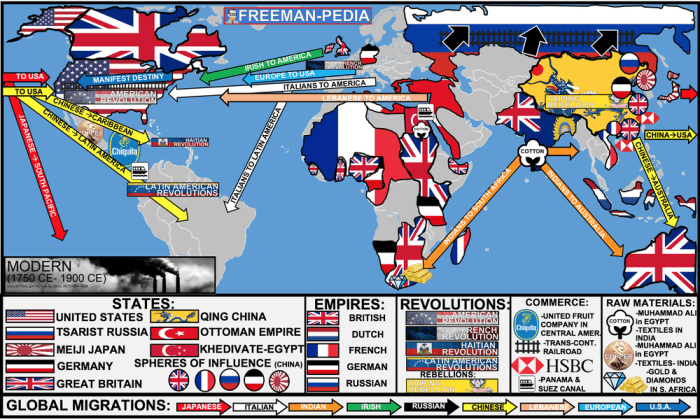
European expansionism in the 18th and 19th centuries was driven by a complex interplay of factors, including the search for new markets, access to raw materials, and the desire for political and economic dominance. The major European powers involved in colonialism were Great Britain, France, Spain, Portugal, the Netherlands, and Belgium.
The forms of colonialism practiced during this period varied widely, from direct rule to indirect rule, from settler colonialism to economic imperialism.
Major European Powers and Their Motivations, Unit 6 imperialism from 1750 to 1900 answers
- Great Britain:Economic expansion, search for new markets, access to raw materials, and strategic advantage.
- France:Economic expansion, rivalry with Great Britain, and desire for political and military power.
- Spain:Economic exploitation, search for gold and silver, and religious conversion.
- Portugal:Economic expansion, search for new trade routes, and access to spices.
- Netherlands:Economic expansion, trade, and establishment of trading posts.
- Belgium:Economic expansion, search for new markets, and access to raw materials.
Imperialism in Asia: Unit 6 Imperialism From 1750 To 1900 Answers
European powers colonized large parts of Asia during the 18th and 19th centuries. The major European powers involved were Great Britain, France, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, and Russia.
The methods used by European powers to establish and maintain their colonies in Asia varied depending on the region and the specific power involved. These methods included military conquest, economic coercion, and political manipulation.
Impact of Imperialism on Asian Societies and Economies
- Economic:Exploitation of resources, disruption of traditional economic systems, and introduction of new crops and technologies.
- Political:Imposition of European political systems, suppression of local resistance, and creation of new political elites.
- Social:Introduction of new social hierarchies, disruption of traditional social structures, and spread of Western ideas and values.
- Cultural:Suppression of local cultures, promotion of European culture, and creation of new hybrid cultures.
Imperialism in Africa
The Scramble for Africa in the late 19th century was driven by a combination of economic, political, and strategic factors. The major European powers involved were Great Britain, France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, and Portugal.
The different forms of colonial rule implemented in Africa included direct rule, indirect rule, and settler colonialism. Direct rule involved the imposition of European laws and institutions, while indirect rule allowed local rulers to retain some authority under the supervision of European officials.
Settler colonialism involved the establishment of permanent European settlements in Africa.
Imperialism in the Americas
European powers colonized large parts of the Americas during the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries. The major European powers involved were Spain, Portugal, Great Britain, France, and the Netherlands.
The impact of imperialism on Native American populations was devastating. European diseases, warfare, and displacement decimated Native American populations. The introduction of European agricultural practices and technologies also disrupted traditional Native American economies and ways of life.
Different Forms of Colonial Rule Implemented in the Americas
- Direct rule:Imposition of European laws and institutions, suppression of local resistance, and creation of new political elites.
- Indirect rule:Allowed local rulers to retain some authority under the supervision of European officials.
- Settler colonialism:Establishment of permanent European settlements in the Americas.
Resistance to Imperialism
Resistance to imperialism emerged in various forms during the 18th and 19th centuries. These forms of resistance included armed uprisings, nonviolent protests, and cultural resistance.
The factors that contributed to the success or failure of resistance movements varied depending on the specific context. These factors included the level of organization and support within the resistance movement, the strength of the colonial power, and the international support for the resistance movement.
Impact of Resistance Movements on the Course of Imperialism
- Forced European powers to make concessions and reforms.
- Inspired other resistance movements around the world.
- Contributed to the eventual decline of imperialism.
FAQ Guide
What were the major causes of European expansionism in the 18th and 19th centuries?
The major causes included economic factors (search for new markets and resources), political factors (rivalry and competition among European powers), technological advancements (improvements in shipbuilding and navigation), and ideological factors (belief in the superiority of European civilization).
How did European powers establish and maintain their colonies in Asia?
European powers used a variety of methods to establish and maintain their colonies in Asia, including military conquest, economic coercion, political alliances, and cultural influence.
What were the different forms of colonial rule implemented in Africa?
The different forms of colonial rule implemented in Africa included direct rule (colonies governed directly by the colonizing power), indirect rule (colonies governed through local rulers), and settler colonies (colonies where European settlers established permanent settlements).