Embark on a captivating journey as we delve into the intricate realm of the heart’s anatomy with “Drag the Labels to Identify Structural Components of the Heart.” This interactive exploration empowers you to unravel the mysteries of this vital organ, deciphering its chambers, valves, and protective layers.
Through vivid illustrations and engaging exercises, you will witness the heart’s intricate design and comprehend its crucial role in sustaining life. Prepare to be enthralled as we embark on this educational adventure, empowering you with a profound understanding of the heart’s anatomy.
1. Introduction
The heart, a vital organ, is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. Its complex structure enables it to efficiently perform this essential function.
Identifying the structural components of the heart is crucial for understanding its function and diagnosing and treating cardiovascular diseases.
2. Methods for Identifying Structural Components
Interactive diagrams or simulations are effective tools for identifying heart components.
Using different colors or shapes for labeling helps differentiate between components and enhance visual clarity.
3. Key Structural Components
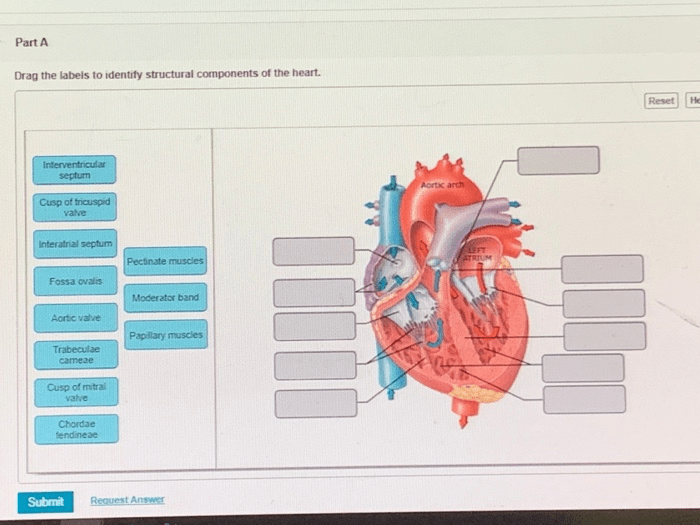
3.1 Major Chambers
The heart consists of four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
The atria receive blood from the body and lungs, while the ventricles pump blood out to the body and lungs.
3.2 Valves
Valves regulate blood flow through the heart, preventing backflow.
The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium and right ventricle, the pulmonary valve separates the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, the mitral valve separates the left atrium and left ventricle, and the aortic valve separates the left ventricle and aorta.
3.3 Pericardium
The pericardium is a sac that surrounds the heart, consisting of two layers:
- Fibrous pericardium:The outer layer, providing structural support.
- Serous pericardium:The inner layer, producing pericardial fluid to reduce friction during heart contractions.
4. Arranging Components in an HTML Table
To create an HTML table with four responsive columns:
- Use the
<table>element withclass="table table-responsive"for responsiveness. - Create four
<thead>elements for column headers. - Create
<tbody>elements for the table body.
Organize components based on their location or function:
- Column 1:Chamber
- Column 2:Valves
- Column 3:Pericardium
- Column 4:Function
5. Using Bullet Points for Procedures
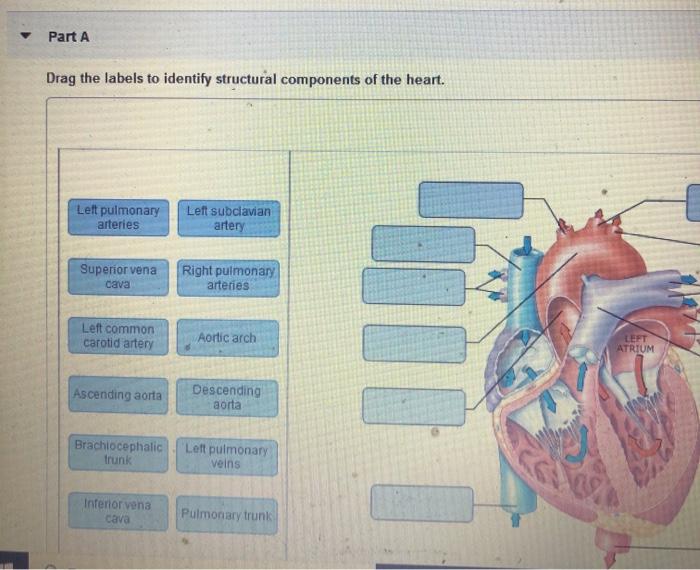
5.1 Procedure for Dragging Labels
- Open the interactive diagram or simulation.
- Identify the labels and their corresponding components.
- Drag and drop the labels onto the correct components.
- Verify that all components are labeled correctly.
6. Illustrating the Heart’s Structure: Drag The Labels To Identify Structural Components Of The Heart.
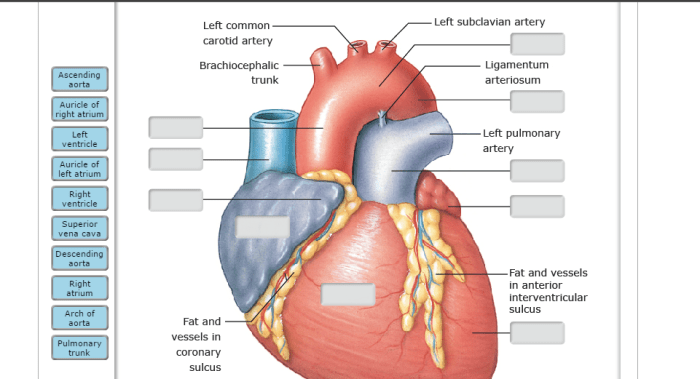
6.1 Chambers
The atria are thin-walled and receive blood from the body (right atrium) and lungs (left atrium).
The ventricles are thicker and more muscular, pumping blood out to the body (right ventricle) and lungs (left ventricle).
6.2 Valves
The valves are thin, flap-like structures that prevent backflow of blood.
They open and close passively, allowing blood to flow in the correct direction.
6.3 Pericardium, Drag the labels to identify structural components of the heart.
The fibrous pericardium is a tough, fibrous layer that provides structural support.
The serous pericardium is a thin, double-layered membrane that secretes pericardial fluid to reduce friction.
Key Questions Answered
How can I use this guide to enhance my understanding of heart anatomy?
This guide provides interactive exercises that allow you to drag labels onto diagrams of the heart, reinforcing your understanding of its structural components.
What are the benefits of using interactive diagrams for learning heart anatomy?
Interactive diagrams provide a hands-on approach to learning, enhancing your engagement and retention of information.
Can I use this guide for educational purposes, such as teaching or self-study?
Yes, this guide is suitable for both educational and self-study purposes, providing a comprehensive overview of heart anatomy.